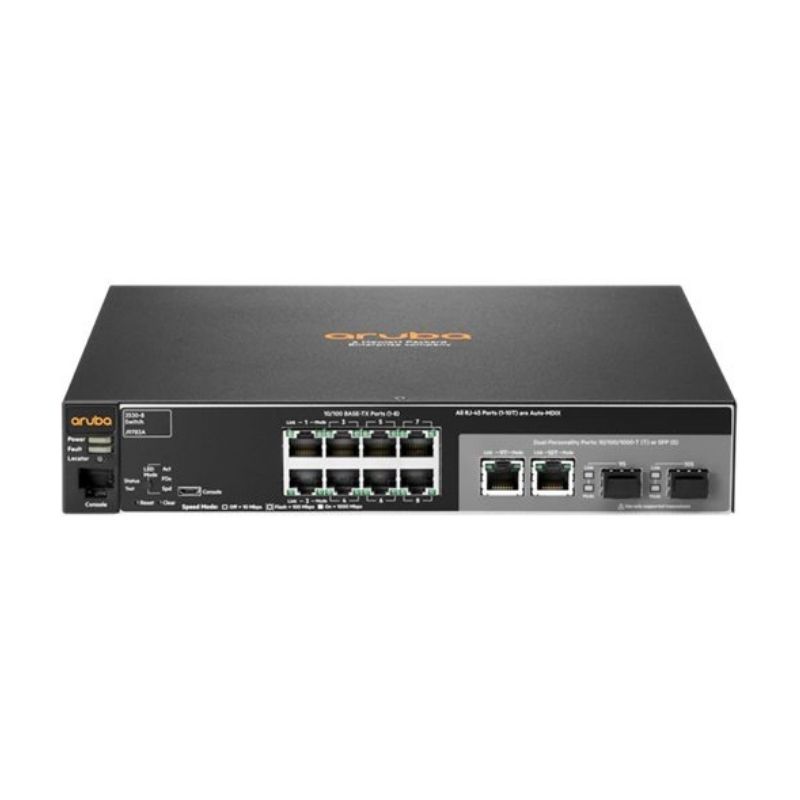
Thiết bị Switch Aruba 2530 8G (J9777A)
Liên hệ báo giá: 0979.300.098
- Hàng chuẩn hãng, bảo đảm nguồn gốc rõ ràng.
- Hỗ trợ tư vấn dự án và giải pháp miễn phí.
- Đồng hành cùng đại lý và các gói dự án lớn nhỏ.
- Cung cấp chứng từ CO/CQ đầy đủ, minh bạch.
- Dịch vụ bán hàng online nhanh chóng, giao hàng toàn quốc.
- Hỗ trợ kỹ thuật chu đáo, sẵn sàng đồng hành cùng khách hàng.

Thông số kỹ thuật
| I/O ports and slots | 8 RJ-45 autosensing 10/100/1000 ports (IEEE 802.3 Type 10BASE-T, IEEE 802.3u Type 100BASE-TX, IEEE 802.3ab Type 1000BASE-T); Media Type: Auto-MDIX; Duplex: 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX: half or full; 1000BASE-T: full only 2 dual-personality ports; each port can be used as either an RJ-45 10/100/1000 port (IEEE 802.3 Type 10Base-T; IEEE 802.3u Type 100Base-Tx; IEEE 802.3ab 1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet) or as a SFP slot (for use with SFP transceivers) ports |
| Additional ports and slots | 1 dual-personality (RJ-45 or USB micro-B) serial console port |
| Physical characteristics | Dimensions: 10(w) x 6.28(d) x 1.75(h) in (25.4 x 15.95 x 4.45 cm) (1U height) Weight: 2.0 lb (0.91 kg) |
| Memory and processor | ARM9E @ 800 MHz, 128 MB flash; Packet buffer size: 1.5 MB dynamically allocated, 256 MB DDR3 DIMM |
| Mounting and enclosure | Mounts in an EIA-standard 19-inch telco rack or equipment cabinet (rack-mounting kit available); Horizontal surface mounting; Wall mounting |
| Performance | 100 Mb Latency < 7.4 µs (LIFO 64-byte packets) 1000 Mb Latency < 2.3µs (LIFO 64-byte packets) Throughut up to 14.8 Mpps (64-byte packets) Switching capacity: 20 Gbps MAC address table size: 16000 entries |
| Environment | Operating temperature: 32°F to 113°F (0°C to 45°C) Operating relative humidity: 5% to 95%, noncondensing Nonoperating/Storage temperature:-40°F to 158°F (-40°C to 70°C) Nonoperating/Storage relative humidity:15% to 95% @ 149°F (65°C), noncondensing Altitude: up to 10,000 ft (3 km) Acoustic: Power: 0 dB, Pressure: 0 dB |
| Electrical characteristics | Frequency: 50/60 Hz Maximum heat dissipation: 203 BTU/hr (214.17 kJ/hr) Voltage: 100 – 240 VAC, rated Maximum power rating: 18.6 W Idle power: 13.6 W Notes: Maximum power rating and maximum heat dissipation are the worst-case theoretical : maximum numbers provided for planning the infrastructure with fully loaded PoE (if equipped), 100% traffic, all ports plugged in, and all modules populated |
| Safety | UL 60950-1; CAN/CSA 22.2 No. 60950-1; EN 60825; IEC 60950-1; EN 60950-1 |
| Emissions | FCC Class A; EN 55022/CISPR-22 Class A; VCCI Class A |
| Management | IMC – Intelligent Management Center; command-line interface; Web browser; configuration menu; out-of-band management (serial RS-232C or Micro USB); IEEE 802.3 Ethernet MIB; Repeater MIB; Ethernet Interface MIB, aruba switch configuration guide, aruba switch default enable password |
Các tính năng hỗ trợ trên switch Aruba J9777A
| Unified Wired and Wireless | Software-defined networking support: leverages REST APIs to enable automation of network operations, monitoring, and troubleshooting
Supports unified wired and wireless policies: using Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager Switch auto-configuration: automatically configures switch for different settings such as VLAN, CoS, PoE max power, and PoE priority when an Aruba access point is detected User role: defines a set of switch-based policies in areas such as security, authentication, and QoS. A user role can be assigned to a group of users or devices, using local switch configuration (YA releases only). |
| Quality of Service (QoS) | Traffic prioritization (IEEE 802.1p): allows for real-time traffic classification. Supports eight priority levels mapped to either two or four queues, and uses weighted deficit round robin (WDRR) or strict priority Simplified QoS configuration Port-based: traffic prioritization by specifying a port and priority level VLAN-based: traffic prioritization by specifying a VLAN and priority level Class of Service (CoS): sets the IEEE 802.1p priority tag based on IP address, IP Type of Service (ToS), Layer 3 protocol, TCP/UDP port number, source port, and DiffServ Rate limiting: establishes per-port ingress-enforced maximums for all traffic or for broadcast, multicast, or unknown destination traffic Layer 4 prioritization: enables priorities based on TCP/UDP port numbers |
| Simplified Configuration and Management | Aruba Central cloud-based management platform: offers a simple, secure and cost effective way to manage switches. Complies with RFC 7030 for encryption key enrollment
Zero-Touch ProVisioning (ZTP): simplifies installation of the switch infrastructure using DHCP-based process with AirWave Choice of management interfaces HTML-based easy-to-use Web GUI Robust CLI Simple network management protocol (SNMPv1/v2c/v3) Flexible management: supports both cloud-based Central and on-premise AirWave without ripping and replacing switching infrastructure Virtual stacking: provides single IP address management for up to 16 switches sFlow (RFC 3176): delivers wire-speed traffic accounting and monitoring, configured by SNMP and CLI with three terminal encrypted receivers IEEE 802.1AB Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP): automates device discovery protocol for easy mapping by network management applications Provides local and remote logging of events: via SNMP (v2c and v3) and syslog; provides log throttling and log filtering to reduce the number of log events generated Port mirroring: allows traffic to be mirrored on any port or a network analyzer to assist with diagnostics or detecting network attacks Remote monitoring (RMON): provides advanced monitoring and reporting capabilities for statistics, history, alarms, and events Find, fix, and inform: finds and fixes common network problems automatically, and then informs the administrator Friendly port names: allows assignment of descriptive names to ports Dual flash images: provides independent primary and secondary operating system files for backup while upgrading Multiple configuration files: are easily stored with a flash image Front-panel LEDs Locator LEDs: allows users to set the locator LED on a specific switch to turn on, blink, or turn off; and simplifies troubleshooting by making it easy to locate a particular switch within a rack of similar switches Per-port LEDs: provides an at-a-glance view of the status, activity, speed, and full-duplex operation Power and fault LEDs: display issues, if any |
| Layer 2 switching | VLANs: supports 512 VLANs and 4,094 VLAN IDs
Jumbo packet support: improves the performance of large data transfers; supports frame size of up to 9,220 bytes 16K MAC address table: provides access to many Layer 2 devices GARP VLAN Registration Protocol: allows automatic learning and dynamic assignment of VLANs Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (RPVST+): allows each VLAN to build a separate spanning tree to improve link bandwidth usage; is compatible with PVST+ |
| Security | Access control lists (ACLs): accommodate IPv4/IPv6 port and VLAN-based ACLs (IPv6 ACL is supported only on Gigabit Ethernet and 48-port models.)
Source-port filtering: allows only specified ports to communicate with each other RADIUS/TACACS+: eases switch management security administration by using a password authentication server Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): encrypts all HTTP traffic, allowing secure access to the browser-based management GUI in the switch Port security: allows access only to specified MAC addresses, which can be learned or specified by the administrator MAC address lockout: prevents particular configured MAC addresses from connecting to the network Multiple user authentication methods IEEE 802.1X: uses an IEEE 802.1X supplicant on the client in conjunction with a RADIUS server to authenticate in accordance with industry standards Web-based authentication: provides a browser-based environment, similar to IEEE 802.1X, to authenticate clients that do not support the IEEE 802.1X supplicant Supports MAC-based authentication: using the client’s MAC address Secure shell (SSH) v2: encrypts all transmitted data for secure remote CLI access over IP networks STP BPDU port protection: blocks Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) on ports that do not require BPDUs, preventing forged BPDU attacks STP root guard: protects the root bridge from malicious attacks or configuration mistakes Secure management access: delivers secure encryption of all access methods (CLI, GUI, or MIB) through SSHv2 and SNMPv3 Custom banner: displays security policy when users log in to the switch Secure FTP: allows secure file transfer to and from the switch; protects against unwanted file downloads or unauthorized copying of a switch configuration file Protected ports CLI: offers intuitive CLI to configure the source-port filter feature, by allowing specified ports to be isolated from all other ports on the switch; the protected port or ports can communicate only with the uplink or shared resources Authentication flexibility Multiple IEEE 802.1X users per port: provides authentication for up to eight IEEE 802.1X users per port; prevents a user from “piggybacking” on another user’s IEEE 802.1X authentication Concurrent IEEE 802.1X, Web or MAC authentication schemes per port: allows a switch port to accept IEEE 802.1X and either Web or MAC authentications Switch management logon security: helps secure switch CLI logon by optionally requiring either RADIUS or TACACS+ authentication DHCP protection: blocks DHCP packets from unauthorized DHCP servers, preventing denial-of-service attacks Dynamic ARP protection: blocks ARP broadcasts from unauthorized hosts, preventing eavesdropping or theft of network data Dynamic IP lockdown: works with DHCP protection to block traffic from unauthorized hosts, preventing IP source address spoofing MAC Pinning: allows non-chatty legacy devices to stay authenticated by pinning client MAC addresses to the port until the clients logoff or get disconnected |
| Convergence | LLDP-MED (Media Endpoint Discovery): defines a standard extension of LLDP that stores values for parameters such as QoS and VLAN to automatically configure network devices such as IP phones
IEEE 802.1AB Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP): facilitates easy mapping using network management applications with LLDP automated device discovery protocol PoE and PoE+ allocations: support multiple methods (automatic, IEEE 802.3at dynamic, LLDP-MED fine grain, IEEE 802.3af device class or user-specified), to allocate and manage PoE/PoE+ power for more energy savings Voice VLAN: uses LLDP-MED to automatically configure a VLAN for IP phones IP multicast (IGMP): prevents flooding of IP multicast traffic LLDP-CDP compatibility: receives and recognizes CDP packets from Cisco’s IP phones for seamless interoperation Local MAC Authentication: assigns attributes such as VLAN and QoS using locally configured profile that can be a list of MAC prefixes |
| Resiliency and high availability | Port trunking and link aggregation
Trunking: supports up to eight links per trunk to increase bandwidth and create redundant connections; and supports L2, L3, and L4 trunk load-balancing algorithm (L4 trunk load balancing is supported only on Gigabit Ethernet and 48-port models.) IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP): eases configuration of trunks through automatic configuration IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree: provides high link availability in multiple VLAN environments by allowing multiple spanning trees; provides legacy support for IEEE 802.1d and IEEE 802.1w SmartLink: provides easy-to-configure link redundancy of active and standby links |
| Product Architecture | Power savings with energy-efficient design
IEEE 802.3az: reduces power consumption during periods of low data activity on Gigabit Ethernet switches Port low power mode: enables the port to automatically go into low-power mode to conserve energy when no link is detected Fanless and variable-speed fans: decrease power consumption in fanless (all 8-port, 2530-24, and 2530-48 PoE+ switches) as well as variable-speed fan switches Port LEDs: conserves energy by optionally turning off port link and activity LEDs Switch on a chip: provides a highly integrated, high-performance switch design with a non-blocking architecture |

 Switch Nettek
Switch Nettek  Switch UniFi
Switch UniFi  Switch Ruckus
Switch Ruckus  Switch Juniper
Switch Juniper  Switch MikroTik
Switch MikroTik  Switch Huawei
Switch Huawei  Switch Fortinet
Switch Fortinet  Switch Draytek
Switch Draytek  Switch Cisco
Switch Cisco  Switch Aruba
Switch Aruba  Switch H3C
Switch H3C  Switch Ruijie
Switch Ruijie  Switch Extreme
Switch Extreme  Switch EnGenius
Switch EnGenius  Converter POE Nettek
Converter POE Nettek  Converter SFP Nettek
Converter SFP Nettek  Converter quang Nettek
Converter quang Nettek  Thiết Bị Quang Công Nghiệp
Thiết Bị Quang Công Nghiệp  Module quang MultiMode
Module quang MultiMode  Module quang SingleMode
Module quang SingleMode  Dây Nhảy Quang Singlemode
Dây Nhảy Quang Singlemode  Dây Nhảy Quang Multimode
Dây Nhảy Quang Multimode  ODF Indoor
ODF Indoor  ODF Outdoor
ODF Outdoor  Bộ lưu điện Nettek Offline
Bộ lưu điện Nettek Offline  Bộ lưu điện Nettek Online
Bộ lưu điện Nettek Online  Cáp Mạng CAT5
Cáp Mạng CAT5  Cáp Mạng CAT6
Cáp Mạng CAT6  Cáp Mạng(AMP)
Cáp Mạng(AMP)  Wifi Unifi
Wifi Unifi  Wifi RucKus
Wifi RucKus  Wifi Huawei
Wifi Huawei  WiFi Cisco Meraki
WiFi Cisco Meraki  Wifi Aruba
Wifi Aruba  Wifi Extreme
Wifi Extreme  Wifi Ruijie
Wifi Ruijie  Wifi MikroTik
Wifi MikroTik  Wifi EnGenius
Wifi EnGenius  Wifi LigoWave
Wifi LigoWave  Wifi Fortinet
Wifi Fortinet  WiFi Everest
WiFi Everest  Wifi H3C
Wifi H3C  Wifi Grandstream
Wifi Grandstream  Wifi Cambium
Wifi Cambium  Tủ Mạng 6U
Tủ Mạng 6U  Tủ Mạng 10U
Tủ Mạng 10U  Tủ Mạng 12U
Tủ Mạng 12U  Tủ Mạng 20U
Tủ Mạng 20U  Tủ Mạng 27U
Tủ Mạng 27U  Tủ Mạng 32U
Tủ Mạng 32U  Tủ Mạng 42U
Tủ Mạng 42U  Tủ Mạng 45U
Tủ Mạng 45U  Firewall Fortigate
Firewall Fortigate  Firewall Barracuda
Firewall Barracuda  Firewall Netgate
Firewall Netgate  Firewall Palo Alto
Firewall Palo Alto  Firewall Huawei
Firewall Huawei  Firewall Cisco
Firewall Cisco  Firewall Sophos
Firewall Sophos  Firewall SonicWall
Firewall SonicWall  Firewall FortiNAC
Firewall FortiNAC  Firewall Zyxel
Firewall Zyxel  Firewall WatchGuard
Firewall WatchGuard  Router MikroTik
Router MikroTik  Router Ubiquiti
Router Ubiquiti  Router Draytek
Router Draytek  Router Teltonika
Router Teltonika  Router Huawei
Router Huawei  Router Ruijie
Router Ruijie  Router H3C
Router H3C  Router Cisco
Router Cisco  Router HPE
Router HPE  Barracuda Load Balancer ADC
Barracuda Load Balancer ADC  Load Balancing Peplink
Load Balancing Peplink  Load Balancing FortiADC
Load Balancing FortiADC  Thiết bị lưu trữ NAS Synology
Thiết bị lưu trữ NAS Synology  Thiết bị lưu trữ NAS QNAP
Thiết bị lưu trữ NAS QNAP  Thiết bị lưu trữ TerraMaster
Thiết bị lưu trữ TerraMaster  Thiết bị lưu trữ NAS ASUSTOR
Thiết bị lưu trữ NAS ASUSTOR  Dell EMC Data Storage
Dell EMC Data Storage  Ổ cứng Synology
Ổ cứng Synology  Ổ cứng Toshiba
Ổ cứng Toshiba  Ổ cứng Seagate
Ổ cứng Seagate  SSD Samsung
SSD Samsung  Ổ cứng Western Digital
Ổ cứng Western Digital  Server Dell
Server Dell  Server HPE
Server HPE  Modem Gateway 3G/4G công nghiệp
Modem Gateway 3G/4G công nghiệp  LoRaWan
LoRaWan  Máy tính công nghiệp
Máy tính công nghiệp  Bộ chia quang
Bộ chia quang  Phụ Kiện Quang
Phụ Kiện Quang  Măng Xông Quang
Măng Xông Quang  Bộ Dụng Cụ Làm Quang
Bộ Dụng Cụ Làm Quang 
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.